Table of Content
- What Is Outsourcing
- Why Companies Choose to Outsource
- Types of Outsourcing
- How Outsourcing Works
- When Outsourcing Makes Strategic Sense
- Challenges and Risks in Outsourcing
- Making Smart Outsourcing Decisions
- Success Through Strategic Implementation
- The Impact of Outsourcing on Jobs and Economy
- Future Trends and Prospects in Outsourcing
- Final Remarks
- Frequently Asked Questions
Business owners face a constant challenge: how to grow efficiently while controlling costs.
Whether you're struggling with overwhelming administrative tasks, lack specialized skills in-house, or find your team stretched thin, there's a strategic solution that's helped countless companies scale successfully.
That solution is outsourcing.
What Is Outsourcing
Outsourcing is the practice of engaging an external entity to perform services or create goods that an organization traditionally handled in-house.
Rather than hiring employees directly, companies transfer specific operations, processes, or functions to third-party service providers who typically operate with different compensation structures and often at lower costs.
Think of it as strategic delegation. Instead of trying to be experts at everything, businesses focus on what they do best while trusted partners handle the rest.
The concept has evolved far beyond simple cost-cutting. Modern outsourcing serves as a strategic management tool that allows companies to reallocate internal resources to core competencies, access specialized capabilities, and enhance overall business agility.
Why Companies Choose to Outsource
The reasons businesses turn to outsourcing vary, but several key drivers consistently emerge:
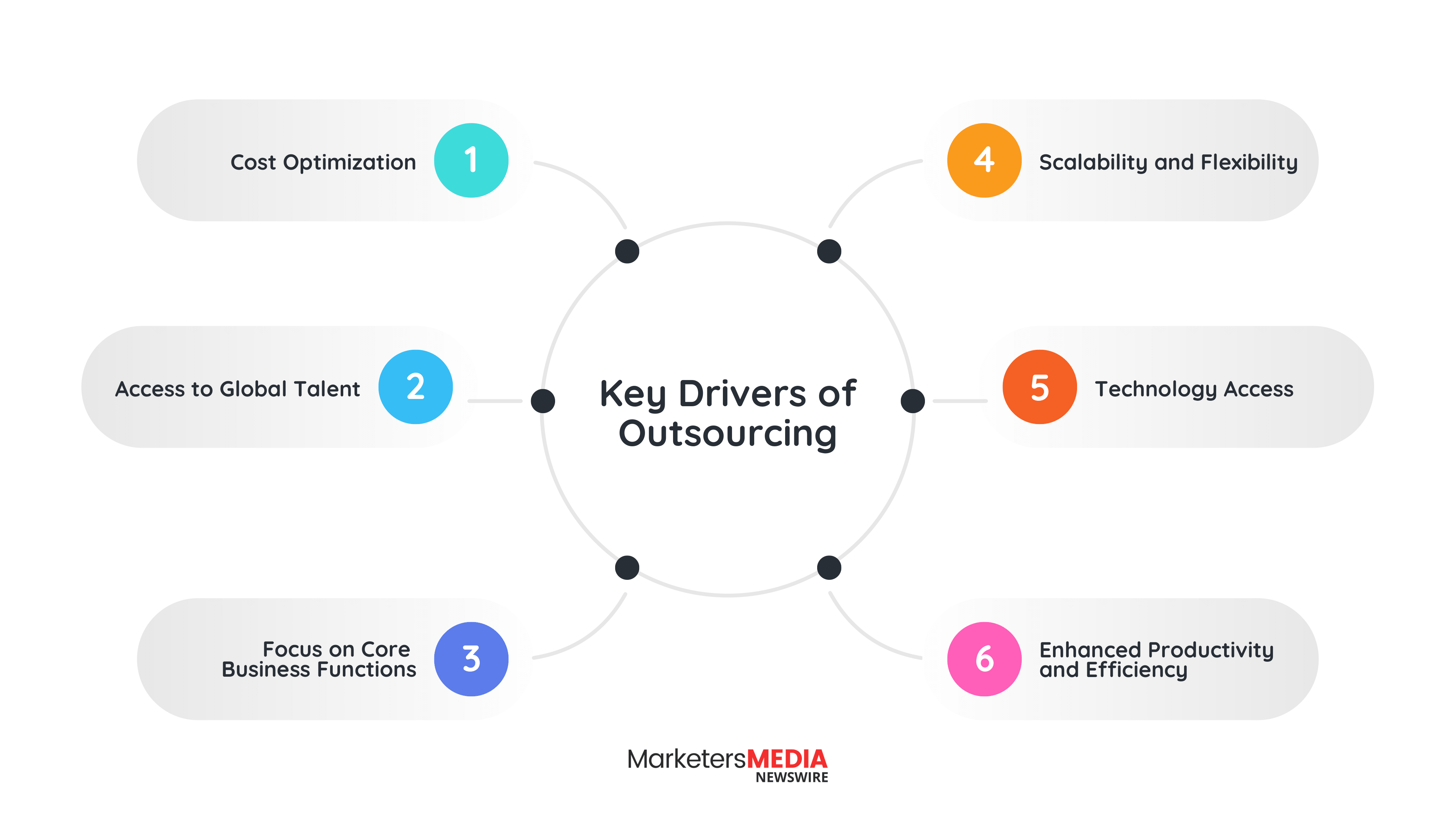
Cost Optimization
The most immediate benefit involves reducing operational and labor expenses. External providers often deliver services at a fraction of what it costs to maintain in-house teams, especially when factoring in salaries, benefits, training, and overhead.
Access to Global Talent
Outsourcing opens doors to skilled professionals worldwide. Companies gain access to expertise that might be scarce or expensive in their local markets.
Focus on Core Business Functions
By delegating non-core tasks to specialists, internal teams can concentrate on activities that directly drive competitive advantage and revenue growth.
Scalability and Flexibility
Outsourcing provides the ability to scale operations up or down quickly without significant investment in infrastructure or long-term commitments to additional staff.
Technology Access
Many outsourcing providers offer access to cutting-edge technology and tools that would be cost-prohibitive for individual companies to purchase and maintain.
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
By leveraging the expertise, tools, and streamlined processes of outsourcing providers, businesses can often achieve higher output with fewer resources. This leads to faster turnaround times, improved service quality, and better use of internal team capacity.
Types of Outsourcing
Understanding the different types of outsourcing helps businesses choose the right approach for their specific needs.
By Location
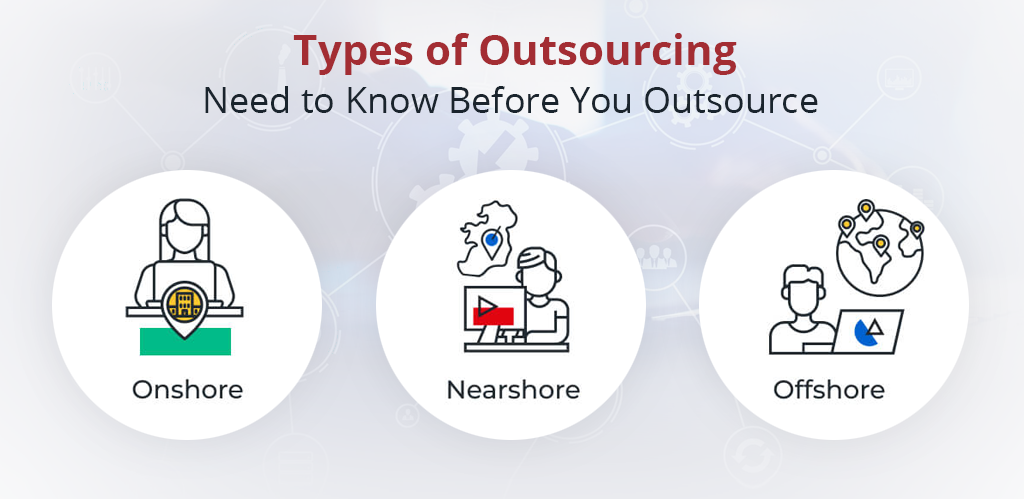
Onshore Outsourcing: Delegating tasks to organizations within the same country or geographical region. While costs may be higher, businesses benefit from skilled workforces with minimal cultural or linguistic barriers.
Nearshore Outsourcing: Partnering with companies in nearby countries that share similar languages, skills, and cultural characteristics. This approach balances cost savings with easier communication and collaboration.
Offshore Outsourcing: Entrusting tasks to organizations in distant countries, typically offering skilled labor at substantially lower costs. This model maximizes cost savings but may introduce communication and cultural challenges.
By Function
Front-Office Outsourcing: Covers customer-facing activities including customer service, sales, telemarketing, and technical support. These functions directly impact customer experience and brand perception.
Back-End Outsourcing: Involves administrative functions like accounting, finance, human resources, and IT support. These essential but non-customer-facing tasks keep operations running smoothly.
IT Outsourcing (ITO): One of the most popular outsourcing categories, covering software development, system maintenance, cybersecurity, and technical support. Nearly every business relies on technology, making ITO widely applicable.
Professional Outsourcing: Encompasses specialized services such as legal work, accounting, purchasing, and administrative support. Companies pay only for services rendered while accessing high-quality expertise.
By Industry Focus
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): Involves outsourcing entire business processes like customer service, payroll processing, or data entry to specialized service providers.
For example, a company might outsource customer service operations or call center services for better customer support and improve response times.
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO): Focuses on knowledge-based tasks requiring high expertise, including data analysis, research and development, and intellectual property management.
Organizations leverage KPO services when they require advanced expertise beyond their internal capabilities. For instance, a pharmaceutical company might outsource drug research and development processes to access industry-specific knowledge.
How Outsourcing Works
Successful outsourcing follows a structured approach:
1. Identifying Opportunities
Define what you aim to achieve through outsourcing, whether it's cost reduction, access to specialized skills, or improved efficiency.
For example, a tech firm might outsource its digital marketing efforts to an agency with expertise in the field.
2. Assess Internal Capabilities
Determine which functions are core to your competitive advantage and which are candidates for external delegation.

3. Define Requirements
Specify project details, expectations, deliverables, and success metrics with precision.
4. Select Service Providers
Research potential partners, considering their reputation, experience, pricing models, and cultural fit.
Evaluate potential partners based on their track record of delivering quality services within set budgets and timelines. This process ensures the client company finds a partner aligned with its goals.
Companies often conduct thorough research before finalizing an outsourcing agreement. They compare different vendors' proposals to determine which one offers the best value for their specific needs.
5. Establishing Contracts
Contracts play a crucial role in outsourcing agreements by outlining key details like scope of work, deliverables, timelines, and payment terms. These documents serve as guidelines for both parties involved in the partnership.
By clearly defining expectations upfront, contracts help prevent misunderstandings or disputes later on during the project execution phase.
6. Implement and Monitor
Establish communication channels, track performance against agreed metrics, and maintain regular oversight.
When Outsourcing Makes Strategic Sense
Certain situations signal that outsourcing might be the right strategic move for your business:
Overwhelming Workloads: When existing employees can't perform their primary jobs due to being burdened by secondary tasks, or when rapid growth outstrips internal capacity.
Skills Gaps: If your company needs specific expertise that current employees don't possess, outsourcing provides immediate access to specialized knowledge.
Resource Constraints: When teams experience burnout, work excessive hours, or neglect essential tasks due to time limitations.
Technology Requirements: If tasks require specialized technology that would be expensive to purchase and maintain internally
Challenges and Risks in Outsourcing
No business strategy is without potential drawbacks. Understanding these challenges helps in preparation and mitigation:
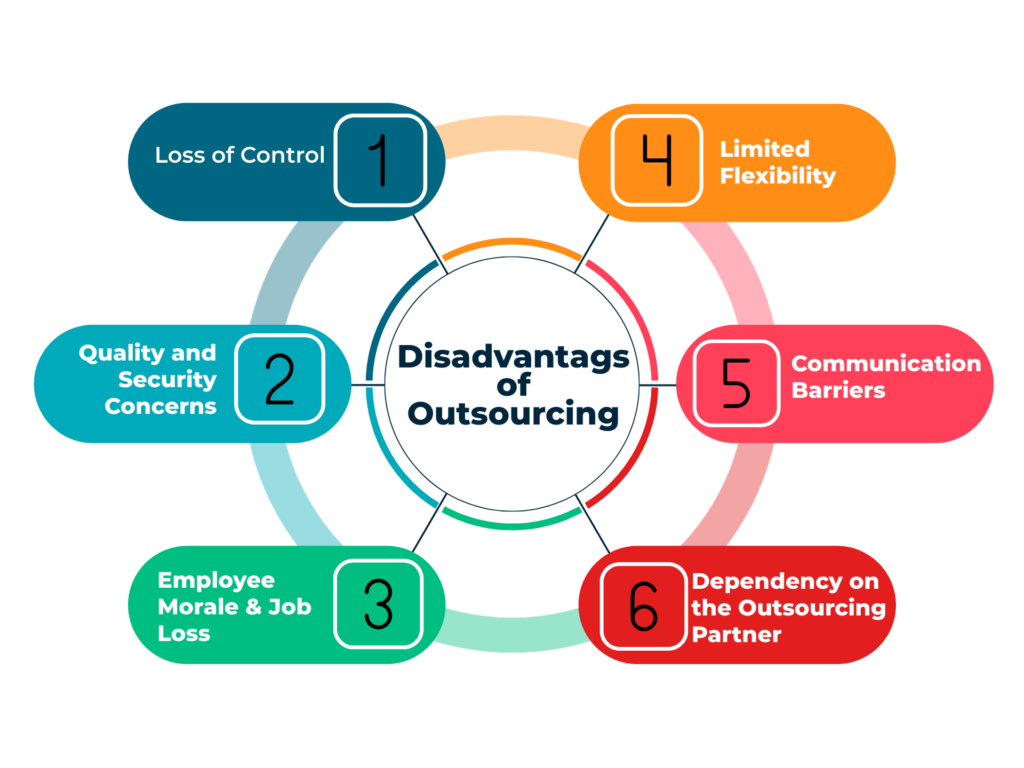
Loss of Direct Control
Delegating functions to external providers naturally reduces direct oversight. Address this by establishing clear service level agreements, regular reporting, and maintaining open communication channels.
Data Security Risks
Sharing sensitive information with external parties during outsourcing poses potential security threats if proper safeguards are not implemented. Companies must establish robust data protection protocols and ensure that all parties involved adhere strictly to these guidelines. Failure to address data security risks adequately could result in breaches leading to financial losses or reputational damage.
- Implement robust data encryption protocols.
- Conduct regular security audits on systems handling sensitive information.
- Provide comprehensive training on data security best practices for all employees involved in outsourcing projects.
- Establish clear contractual agreements outlining data protection responsibilities between both parties.
Communication Barriers
Effective communication between the client and the outsourced team can be hindered by language differences or time zone variations. This can lead to misunderstandings, delays in project timelines, and overall inefficiency. To mitigate this challenge, companies often invest in tools like video conferencing platforms or project management software to bridge the communication gap.
- Risks: Misunderstandings, delays, inefficiency
- Disadvantages: Language barriers, time zone differences
- Examples: A company based in the United States outsourcing tasks to a team located in India may face challenges due to significant time zone variations.
Quality Control Issues
Ensuring consistent quality across outsourced services is crucial but can be challenging. Additional monitoring mechanisms and performance metrics need to be established to maintain high standards. Regular audits of the outsourced processes are essential to identify any deviations from quality expectations promptly.
- Risks: Inconsistent quality, lack of control
- Challenges: Monitoring mechanisms, performance metrics
- Examples: A business outsourcing customer service operations must implement strict quality control measures to uphold service standards consistently.
Employee Morale Impact
Internal staff may worry about job security when outsourcing begins. Address concerns through transparent communication about how outsourcing supports growth rather than replaces people.
Making Smart Outsourcing Decisions
Before committing to outsourcing, consider these critical questions:
- How far from your core functions is this specific task?
- Does direct control over this function matter for strategic reasons?
- Will this allow for better scalability and flexibility?
- What are the total costs, including hidden expenses like transition and management?
- Can you effectively manage potential risks?
These questions help establish whether outsourcing aligns with your strategic objectives and risk tolerance.
Success Through Strategic Implementation
For businesses new to outsourcing, starting small proves most effective. Begin with non-critical tasks to test processes and build relationships before expanding to more significant functions.
Choose Initial Projects Wisely
Focus on projects with clear deliverables and measurable outcomes. This approach allows you to refine your outsourcing processes while minimizing risk.
Partner Selection Matters
Find partners who understand your industry and demonstrate strong communication skills. Cultural fit matters as much as technical expertise for long-term success.
Content and Communication Outsourcing
Many businesses find success outsourcing content creation and marketing communications. Tools like SurgeGraph help companies scale content production without sacrificing quality, creating long-form, SEO-optimized articles that sound natural and reflect brand voice clearly.
For companies needing broader market reach, services like MarketersMEDIA Newswire provide guaranteed pickup across 550+ media outlets with 5.9B total potential reach, serving 160 countries—demonstrating how specialized outsourcing can access capabilities far beyond what most companies could build internally.
The Impact of Outsourcing on Jobs and Economy
Job Creation in Outsourcing Destinations
Outsourcing can lead to the creation of new jobs in countries where services are outsourced. For example, a company outsourcing customer service operations to a call center in India would create employment opportunities for individuals in that region.
This influx of job opportunities can stimulate economic growth by providing income for local residents and boosting consumer spending within the community. As more companies outsource their operations to these destinations, it can attract further investments from foreign businesses looking to capitalize on the skilled labor force available.
Job Displacement in Home Countries
Conversely, some argue that outsourcing results in job losses within industries that opt for outsourcing their functions.
When companies decide to outsource certain job functions overseas due to lower labor costs or other factors, employees in the home country may face unemployment or have to transition into different roles within the organization.
This displacement of domestic jobs has been a point of contention among critics who believe that outsourcing negatively impacts local economies by reducing employment opportunities and potentially lowering wages for remaining workers.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of outsourcing extends beyond just job creation and displacement. By engaging in outsourcing practices, companies can benefit from cost savings which could be redirected towards innovation and expansion efforts.
Moreover, when firms outsource certain tasks internationally, they contribute to fostering global trade relationships between countries involved. This cross-border collaboration not only enhances efficiency but also opens up avenues for increased investment flows across borders leading to overall economic development.
Future Trends and Prospects in Outsourcing
Automation and Artificial Intelligence

Outsourcing is changing rapidly due to increased adoption of automation and AI. These technologies are revolutionizing how tasks are completed, making processes more efficient. For example, routine customer service inquiries can now be handled by chatbots, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. This shift allows companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
Pros:
- Enhanced efficiency in completing tasks.
- Reduction in operational costs.
Cons:
- Potential job displacement due to automation.
- Initial high cost of implementing advanced technologies.
Niche Outsourcing Services
The demand for specialized outsourcing services like cybersecurity or data analytics is on the rise. Companies are seeking expertise beyond traditional functions to gain a competitive edge. By outsourcing niche services, businesses can access specialized skills that may not be available in-house. For instance, a company handling sensitive customer data might outsource cybersecurity services to ensure robust protection against cyber threats.
Key Information:
- Access to specialized skills not available internally.
- Competitive advantage through expert services.
Ethical Sourcing Practices
Ethical considerations are becoming central in the outsourcing landscape. Companies are placing greater emphasis on social responsibility and sustainability when selecting suppliers. By partnering with ethical suppliers who adhere to responsible practices, organizations can enhance their reputation and mitigate risks associated with unethical behavior within their supply chain.
Examples:
- Choosing suppliers with fair labor practices.
- Ensuring environmental sustainability throughout the supply chain.
Statistics on Outsourcing
Growth of the Global IT Outsourcing Market: The IT outsourcing market is a significant component of the global outsourcing industry, showcasing remarkable growth. By 2026, it is projected that the global IT outsourcing market will reach a valuation of $425.19 billion, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026. This expansion reflects the increasing reliance on IT outsourcing by businesses aiming to leverage specialized skills and technologies to drive their operations forward.
IT Outsourcing Spend: Looking into the near future, IT outsourcing spend is anticipated to surpass $1.3 trillion by the end of 2023. This statistic underscores the vital role of IT services in the modern business ecosystem, where companies continually seek cost-effective solutions to enhance their technological capabilities. The surge in demand for Software as a Service (SaaS) and cloud solutions is a key driver behind this growth, demonstrating the shift towards more flexible and scalable IT service models.
Final Remarks
Outsourcing has evolved from a simple cost-cutting tactic to a sophisticated strategic tool for business optimization. Companies that approach it thoughtfully—with clear objectives, careful partner selection, and robust management processes—often discover it becomes a cornerstone of their growth strategy.
The key lies in viewing outsourcing not as giving up control, but as gaining access to specialized expertise while freeing internal resources to focus on what truly drives competitive advantage.
Whether you're a startup looking to scale quickly or an established company seeking operational efficiency, outsourcing offers a proven path to achieve your goals while maintaining focus on your core mission.
Success in outsourcing starts with understanding your needs, researching your options, and taking measured steps toward building productive partnerships that support long-term growth. The companies that master this approach often find themselves better positioned to compete in an increasingly complex business environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the basic concept of outsourcing?
Outsourcing involves delegating specific tasks or services to external third-party providers rather than handling them in-house. It allows companies to focus on core activities while benefiting from specialized expertise and cost-efficiency.
How does outsourcing benefit businesses?
Outsourcing offers advantages such as cost savings, access to specialized skills, increased efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. By partnering with external experts, businesses can streamline operations and enhance their overall performance.
Are there risks associated with outsourcing?
Yes, some common risks include data security concerns, communication challenges due to geographical differences, quality control issues, dependency on the service provider's reliability, and potential loss of managerial control over outsourced functions.
What distinguishes outsourcing from offshoring?
While both involve delegating tasks externally, outsourcing refers to contracting any business function regardless of location. Offshoring specifically entails relocating business processes or services to a different country for reasons like cost savings or accessing global talent pools.
How can businesses ensure successful outsourcing strategies?
To succeed in outsourcing initiatives, it's crucial for businesses to define clear objectives upfront; choose reliable partners through thorough vetting processes; establish robust communication channels; monitor performance regularly; and adapt strategies based on feedback for continuous improvement.
Free Press Release Template
Tell us where to send your PDF: